What is Thermography?
How Does Thermography Work?
Applications in Pain Detection
- Chronic Pain Management: Thermography is particularly useful in diagnosing chronic pain conditions. It helps in identifying the exact location and extent of pain, which is crucial for effective treatment planning. Conditions like arthritis and complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) can be better managed with the insights provided by thermal imaging (1).
- Injury Assessment: For sports injuries or trauma, thermography can quickly assess the severity and location of the injury. This allows for timely intervention and can help in monitoring the healing process (1).
- Nerve Damage Detection: Thermography is effective in detecting nerve damage, which often presents as abnormal heat patterns. This can be particularly beneficial for conditions like neuropathy, where early detection can significantly impact treatment outcomes (1).
Case example: Pain detection
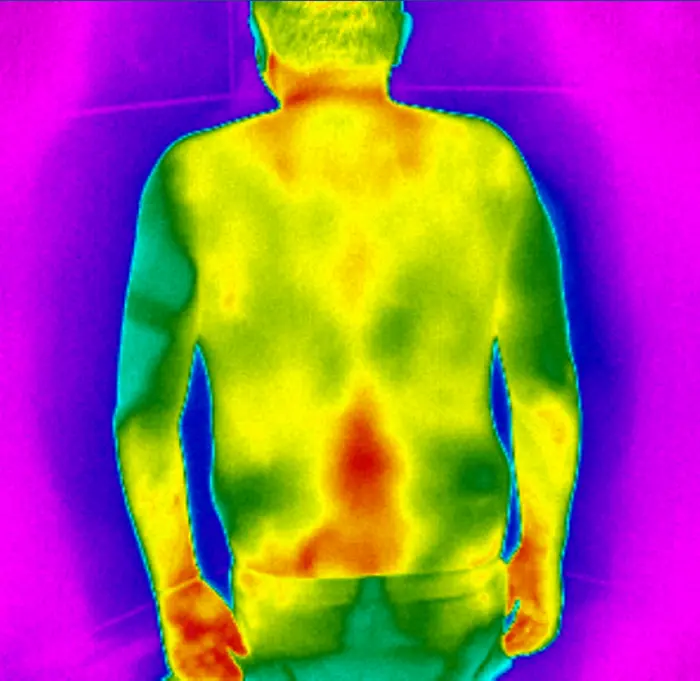
The patient had visited multiple doctors complaining about the pain in his back. Pain radiates to the left side and is visible in the thermal image.
The cause was found to be a pinched nerve between the L4 and L5 vertebrae.
This thermal image was taken and analyzed using an IRT-384 Tablet.
Advantages of Thermography
- Non-Invasive: Unlike other imaging techniques, thermography does not require any physical contact or radiation exposure, making it a safe option for repeated use.
- Real-Time Results: Thermal images are generated in real-time, providing immediate insights that can guide further diagnostic steps or treatments.
- Cost-Effective: Thermography is relatively affordable compared to other imaging modalities like MRI or CT scans, making it accessible for a broader range of patients (1).
(1) Kesztyüs D, Brucher S, Kesztyûs T. Use of infrared thermography in medical diagnostics: a scoping review protocol BMJ Open 2022;12:e059833. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059833
(2) Kesztyüs, D.; Brucher, S.; Wilson, C.; Kesztyüs, T. Use of Infrared Thermography in Medical Diagnosis, Screening, and Disease Monitoring: A Scoping Review. Medicina 2023, 59, 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122139
(3) Etehadtavakol, M., Ng, E.Y.K. (2017). Potential of Thermography in Pain Diagnosing and Treatment Monitoring. In: Ng, E., Etehadtavakol, M. (eds) Application of Infrared to Biomedical Sciences. Series in BioEngineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3147-2_2