IRT-384 Tablet
All-in-one mobile solution for thermal imaging including a high-resolution thermal camera and VistaClinic software.
FDA Cleared
CE Certified
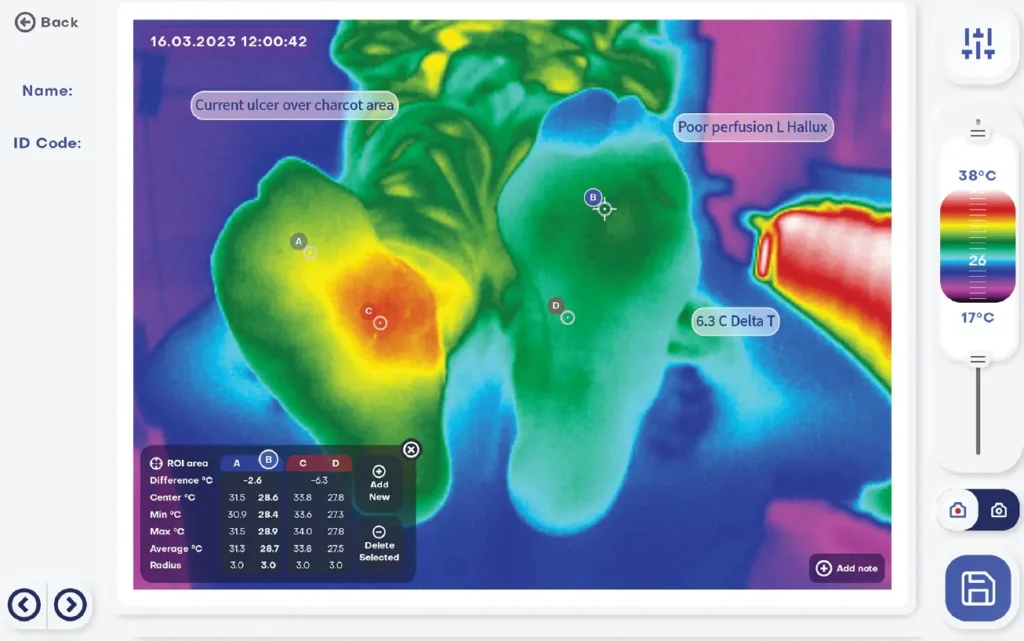
A trial run of a Thermidas thermal imaging system was conducted in a Finnish care home in May-June 2024. All the participating workers were positive that thermal imaging will make risk assessment and prevention of pressure ulcers significantly easier.
The application of infrared thermography into routine pressure injury risk assessment provides a timely and reliable method for nursing practitioners. Infrared thermography has great value of clinical application in daily pressure injury assessment. It is of great significance to make a faster and more objective clinical judgement for patients at risk of pressure injury
Fuman Cai, 2020. Application of infrared thermography in the early warning of pressure injury: a prospective observational study
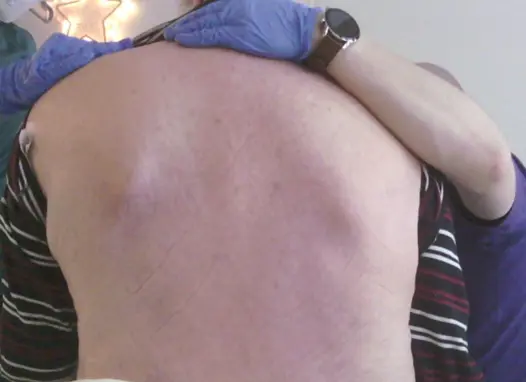
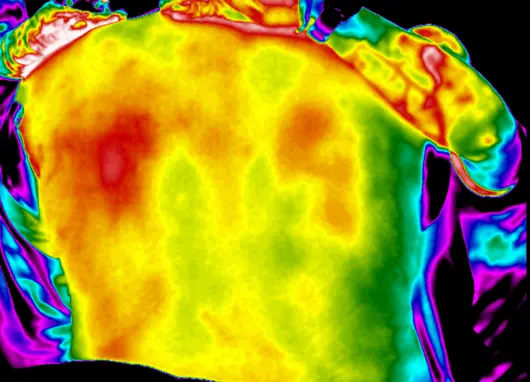
In the aforementioned study, 415 patients admitted to the adult intensive care units were enrolled by a convenience sampling method, and they received a follow-up monitoring for 10 days.
The risk of pressure injury was assessed via Braden scale, and thermal images of the sacral area were obtained by infrared thermal imager once a day.


All-in-one mobile solution for thermal imaging including a high-resolution thermal camera and VistaClinic software.
FDA Cleared
CE Certified

We use the device for a large number of cases and our experiences have been very positive. We can recommend the device for various clients.
Stefanie Ott
Dominikus-Ringeisen-Werk
Jiang et al, 2022. Application of an infrared thermography-based model to detect pressure injuries: a prospective cohort study
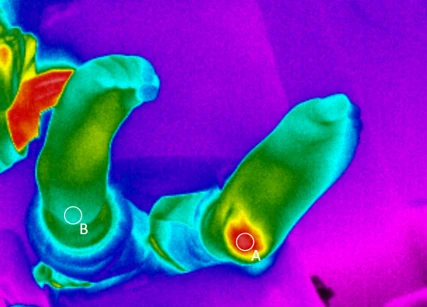
A recent study from China included 263 patients who were screened for pressure injuries in the sacral region. The study showed that the ability of infrared thermography to detect pressure injuries was better than that of the other methods used.